Atomic Layer Deposition for Additive Manufacturing – Metal 3D Printing

Summary
Atomic layer deposition (ALD) on metal powder feedstock materials for 3D printing can provide significant improvements in the final printed product. By using ALD to deposit a thin, conformal coating onto the metal powder particles before printing, it is possible to improve the flowability of the powder, which can lead to more consistent printing and reduced defects.
In addition, ALD can provide moisture and oxidation resistance to the metal powder, which can help to reduce waste and improve the quality of the printed parts. By reducing the amount of oxidized metal powder byproduct during the printing process, it is possible to improve the efficiency and sustainability of the 3D printing process.
ALD can also improve the sintering interfaces between metal powder particles, which can lead to stronger, more durable printed parts. And by reducing inclusions in the bulk printed material, ALD can help to improve the quality and performance of the final product.
Overall, ALD on metal powder feedstock materials for 3D printing has the potential to significantly improve the quality and efficiency of the 3D printing process, and may play an important role in the continued growth of the metal 3D printing market.
ALD improves Metal 3D Printing Products
The benefits of ALD layers:
ALD for Flowability
Variability in feedstock properties can indeed lead to uneven layering of particles in a powder bed, which can result in inconsistent bulk density and ultimately lead to lower tensile strength products and hot tearing of material. This is particularly true for metal powders used in 3D printing, where powder flowability is critical for achieving high-quality, defect-free parts.
ALD can improve the flowability of powder without chemically changing the bulk particle. This is because the ALD coating is a thin layer of material that is deposited on the surface of the particles, which does not affect the bulk properties of the material. In a 2019 study, TiO2 ALD was used to improve the flowability of partially crystalline and amorphous materials, and the results showed a significant improvement in flowability after just five ALD layers.
It’s worth noting that ALD can be used not only to improve flowability but also to address other issues related to metal powder feedstock materials, as mentioned earlier. For example, ALD can improve the moisture and oxidation resistance of the powder, reduce the presence of inclusions in the final product, and improve the sintering interfaces between the metal powder particles during the printing process.
Overall, ALD is a promising technique for improving the quality and consistency of metal powder feedstock materials used in 3D printing, and its potential applications are vast.
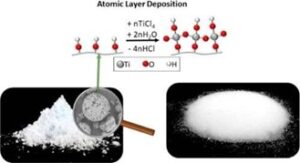
Image 1: Five cycles of TiO2 ALD performed on powders to quadruple or triple flowability
Please click on ‘Request Application Note’ and we will send you the full application note: ‘Atomic Layer Deposition for Additive Manufacturing – Metal 3D Printing’.