Applications for potentiostats / galvanostats / EIS
Metallic surfaces can corrode while in contact with a corrosive solution (mostly acidic media). By using electrochemical methods you can study the behavior of the metal while submersed in a corrosive solution. Potentiostats / galvanostats are used to characterize the behavior of these metals. Techniques like, e.g., Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS), Linear Polarization Resistance and Tafel Plot experiments are used to characterize the behavior of the metals.
Photovoltaic cells are everywhere these days. Solar energy is important in local, regional and national energy production. To improve the efficiency of such an energy supply, a lot of research is done. Photovoltaic solar cells characterization can be performed by polarization and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy techniques, which allow the user to determine cell performance and model. The contribution of the electrochemistry in energy fields is currently a hot topic.
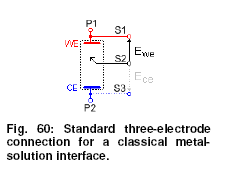
Understanding the kinetics and the thermodynamics of a reaction occurring on an electrode is the general purpose of fundamental electrochemistry. Potentiostats / galvanostats and EIS are essential tools in this field. In this application, DC steady-state methods have been used such as: cyclic voltammetry, chronoamperometry, chronocoulometry, chronopotentiometry, pulse voltammetry, square wave voltammetry and other current-potential techniques.