The effect of salt deposition on the performance of floating PVs
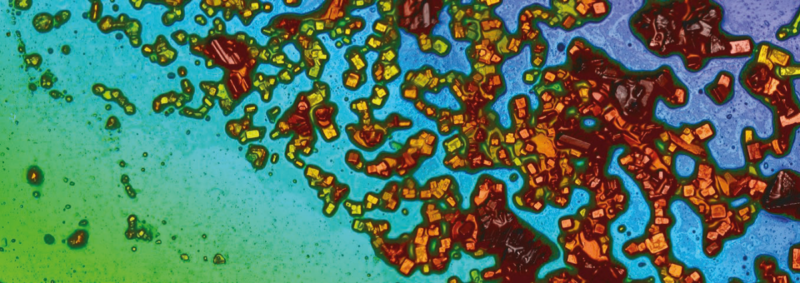
Floating photovoltaic installations are a new concept combining land-based PV technology with novel floating systems. A number of floating PV installations have been implemented at a global level on various types of fresh water bodies including lakes, as well as irrigation and agricultural ponds. For small islands like Malta, surrounded by saline territorial waters, one must also take into account the potential effect of salt deposition on the performance of floating solar PV systems when considering offshore installations. To extract the full potential of such a solar energy system, efficiency and performance should be at the highest possible levels, thus the number of factors that can affect these two measures should be examined and taken into consideration. Dust accumulation on PV panels is widely known to significantly reduce performance; the effect of salt, on the other hand, has not been investigated. Since salt is not as opaque as dust, it is not clear how much it would shade PVs or to what extent it would accumulate after repeated panel wetting.
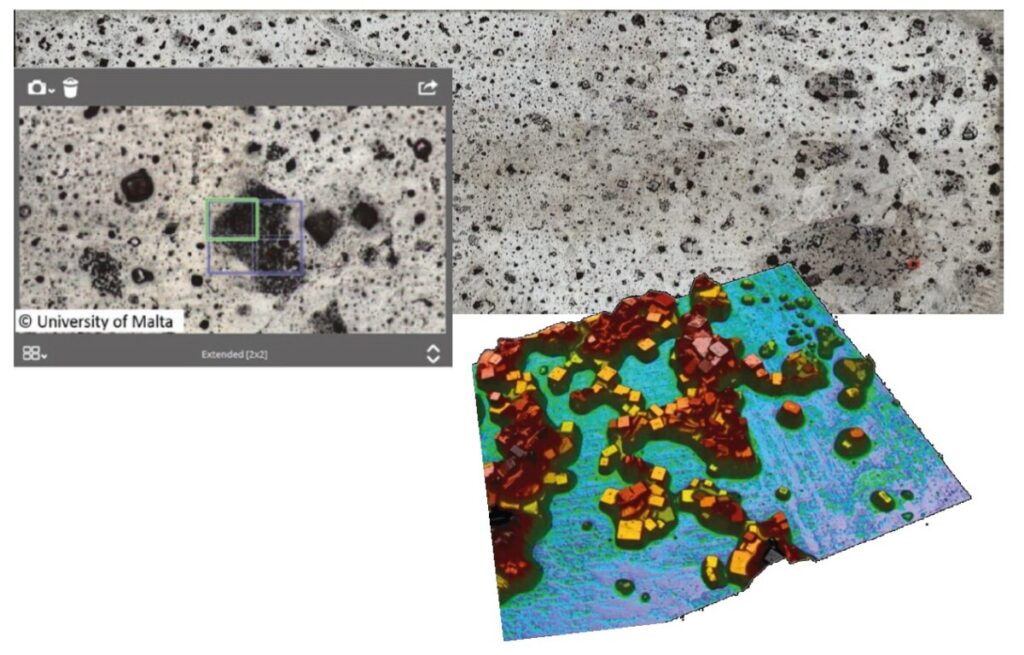
A sequence of wetting tests with solutions of various salt concentrations are being carried out in conjunction with opacity testing and light transmission testing to investigate the performance of PVs when exposed to a marine environment. White light optical profilometry in conjunction with microscopy is used to obtain the thickness measurements of the deposited salt layer in order to measure how long panels can be exposed to salt solutions with no adverse effects.
Please click on ‘Request Application Note’ and we will send you the full application note: ‘The effect of salt deposition on the performance of floating PVs’.